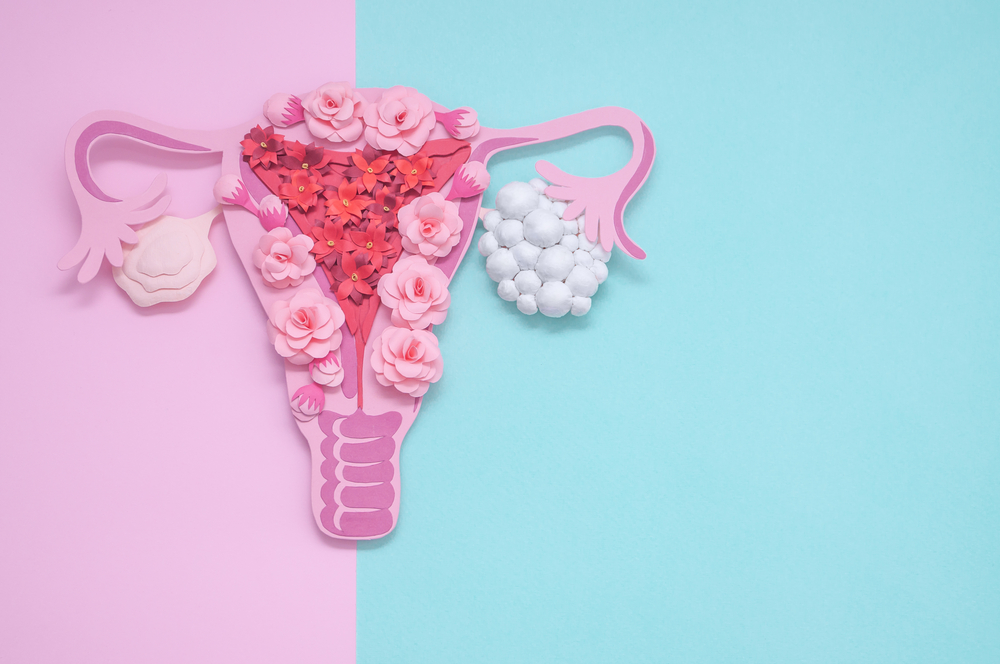
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine condition that affects many women worldwide. Characterized by the presence of ovarian cysts, hormonal imbalances, and other clinical signs, PCOS can impact women’s reproductive and overall health. In this article, we will explore Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in detail, including symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
Causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a complex condition, and its causes are not fully understood. However, experts believe that several factors are involved, including:
- Insulin dysfunction: Insulin resistance is often associated with PCOS. In this condition, the body’s cells do not respond adequately to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and hormonal imbalance.
- Ovarian dysfunction: In women with PCOS, the ovaries can overproduce male hormones called androgens. This can interfere with regular ovulation and lead to the formation of ovarian cysts.
- Genetic factors: Heredity appears to play a role in predisposition to polycystic ovary syndrome. If a woman has first-degree relatives affected by PCOS, she may have a slightly higher risk of developing the condition.
- Elevated levels of gonadotropins: In women with PCOS, levels of gonadotropins, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), can be elevated compared to normal. This can affect ovarian function and contribute to the formation of cysts.
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can present with a wide range of symptoms, which can vary from person to person. Some of the most common PCOS symptoms include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS may experience irregular cycles, heavy menstruation, or missed periods.
- Increased levels of male hormones: The presence of androgens can lead to acne, excessive facial and body hair growth (hirsutism), and thinning of hair on the scalp.
- Fertility issues: Due to irregular or absent ovulation, many women with PCOS may have difficulty conceiving.
- Weight gain: Some women with PCOS may experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight.
- Metabolic issues: PCOS is often associated with a higher likelihood of developing metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart problems.
- Mood changes: Some women with PCOS may experience mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
It’s important to emphasize that not all women with PCOS experience the same symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary significantly from person to person.
Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
The treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is based on symptom management and promoting overall well-being. Some common treatment options for PCOS include:
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can help improve PCOS symptoms. Reducing the intake of simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can be especially helpful in managing insulin resistance.
- Medications: A doctor may prescribe medications to regulate hormone levels, promote ovulation, or improve insulin sensitivity. It’s important to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and discuss any potential side effects or risks associated with the prescribed medications.
- Hormone Therapy: Some women with PCOS may benefit from hormone therapy to balance hormone levels and improve symptoms. This therapy may include the use of birth control pills or other hormonal medications.
- Surgery: In selected cases, when PCOS symptoms are severe and do not respond to other treatments, the doctor may recommend surgeries such as laparoscopy to remove ovarian cysts.
It is important to consult a doctor or specialist for an accurate evaluation and to establish the most suitable treatment plan for your needs.
Polycystic Ovary and Pregnancy
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can impact women’s fertility and pose a challenge when trying to conceive. However, it’s important to emphasize that having PCOS doesn’t necessarily mean it’s impossible to get pregnant. Many women with this condition are able to achieve a healthy pregnancy with the help of appropriate treatments and medical guidance.
Women with polycystic ovaries may face various fertility obstacles, including:
Irregular or absent ovulation: One of the primary challenges for women with PCOS is irregular ovulation or the absence of ovulation. Since ovulation is necessary for conception, this condition can make natural pregnancy more difficult.
Hormone Imbalance: PCOS is characterized by an imbalance in reproductive hormones, with an excessive production of androgens (male hormones) relative to estrogen (female hormones). This imbalance can interfere with the maturation and release of the egg, hindering the ability to conceive.
Metabolic Issues: Insulin resistance, often associated with PCOS, can increase the risk of gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Additionally, women with PCOS may have a higher risk of developing complications such as preeclampsia and premature birth.
Despite these challenges, many women with polycystic ovary syndrome can become pregnant with the appropriate medical support. Here are some treatment options that can be considered:
- Ovulation Stimulation: If women with PCOS do not ovulate regularly, the doctor may prescribe medications to stimulate ovulation. These drugs can help regulate the menstrual cycle and promote the release of a mature egg.
- Ovulation Monitoring: During treatment, the doctor may closely monitor ovulation through transvaginal ultrasounds and hormone level monitoring. This helps identify the most suitable time for sexual intercourse to maximize the chances of conceiving.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): In cases where other treatments are unsuccessful, IVF may be considered as an option. IVF involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs, which are then collected, fertilized in a laboratory, and subsequently implanted into the uterus.
Consulting a fertility specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your needs is crucial. Every woman with PCOS will have a unique situation and will require a personalized approach.
During pregnancy, women with polycystic ovary syndrome may require closer monitoring to manage the risks associated with the condition. It’s important to work closely with a specialist doctor and follow recommended guidelines to ensure a healthy pregnancy and the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Conclusion
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a complex condition that requires careful management. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help women with PCOS make informed decisions about their health. Remember to always consult with a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and to receive the appropriate treatment. PCOS should not be tackled alone but with the help of experienced medical professionals who can provide the guidance and support needed.

 Italiano
Italiano